What are the Signs of Male Menopause?
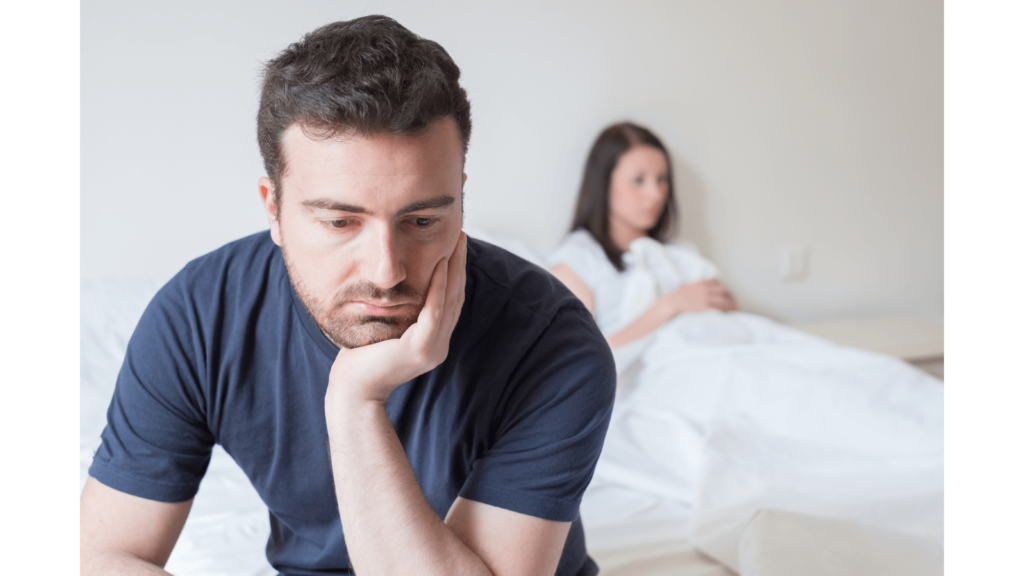
One night while out to dinner with girlfriends, the topic of sex came up, as it often does. One friend hung her head and confessed, “Things aren’t the same in the bedroom with my partner lately. He takes longer to get aroused and sometimes loses interest before we really get going. I don’t know what to do – I ask him if it’s something I’m doing or if something is going on with him that I don’t know about, and he bites off my head. I get that it’s embarrassing to have problems with erections sometimes, but I don’t know how to get through this slump.”
As men age, their bodies undergo numerous changes, including a gradual decline in hormone production. One of the most significant changes is andropause, also known as male menopause. Andropause can lead to several symptoms that significantly affect a man’s physical, mental, and emotional health. Often, men are embarrassed or frustrated by the signs of male menopause and suffer in silence.
Unfortunately, many men are unaware of andropause or available treatment options. This is where bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) comes in. This article will discuss the signs of male menopause, the role of male hormones in ageing, and the benefits of BHRT. Don’t let andropause go untreated – read on to learn how BHRT can help improve your quality of life.
“If menopause is the silent passage, ‘male menopause’ is the unspeakable passage. It is fraught with secrecy, shame, and denial. It is much more fundamental than the ending of the fertile period of a woman’s life because it strikes at the core of what it is to be a man.” – Gail Sheehy
Understanding Andropause
Andropause is brought on by a natural decline in testosterone and other hormones as men age. Unlike menopause in women, andropause occurs more gradually over a longer period. As testosterone levels decrease, men may experience various symptoms that can significantly impact their quality of life. Most think about the sexual issues that low testosterone can cause, but many other body systems are also affected by low testosterone.
Male Hormones and Aging
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for developing muscle mass, bone density, and body hair. Testosterone also plays a critical role in brain health, including focus and memory, sleep quality, emotions, male reproductive health, and sexual function.
Testosterone is responsible for what most consider as stereotypical male traits: larger muscles, lower body fat, competitive drive, physical strength and stamina, and a high libido (sex drive).
Testosterone levels peak during adolescence and early adulthood, and they gradually decline with age. By the age of 30, testosterone levels begin to fall at around 1% per year; by the age of 70, almost 50% of men have testosterone levels below the normal range1.
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) is a protein that helps to control the amount of sex hormones (in this case, testosterone) that are actively working in your body. SHBG increases as men age, which means more testosterone is bound to this protein, and therefore, less is available for the body to use.
As testosterone decreases and SHBG increases, the signs of male menopause can be more noticeable. Men with particularly stressful jobs or unhealthy lifestyles may start experiencing andropause symptoms in their mid-30s, but most men begin noticing symptoms in their late 40s.
What are the Signs of Male Menopause?
Andropause can cause a wide range of symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Reduced muscle mass and strength
- Increased body fat, particularly around the midsection
- Decreased sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Mood swings
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Insomnia
- Memory loss
- Decreased self-confidence
- Night sweats
Studies have also linked andropause to osteoporosis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease2,3,4.
However, low testosterone levels don’t have to be permanent, and you don’t have to be embarrassed about the symptoms you’re experiencing. There are treatment options available that can help you get back to feeling like the man you were before.
Bioidentical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT) for Andropause
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) is a treatment that involves the use of hormones that are identical in molecular structure to the hormones naturally produced by the body. BHRT can help to restore hormone levels to a more balanced state.
Benefits of BHRT for Andropause
BHRT can help to alleviate the symptoms of andropause mentioned above. BHRT may also help to reduce the risk of certain age-related conditions such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and dementia.
BHRT is well tolerated, especially compared to traditional hormone replacement therapy. Many men report increased energy, better sleep, and fewer mood swings within a few weeks. Most symptoms can be improved within a few months.
Conclusion
Andropause is a natural part of the ageing process that can cause a range of symptoms and health concerns. While it’s not always easy to talk about, men need to understand that they’re not alone in experiencing andropause and that safe and effective treatments are available.
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) is an excellent option if you’re experiencing symptoms of andropause and want to balance your hormones. BHRT is personalised to your hormone levels and unique needs. The process involves regular monitoring by a trained practitioner to optimise your hormone levels.
Don’t let andropause hold you back from living your best life. Schedule a consultation with one of our Personalised BHRT Specialist Doctors about your options for treating andropause and take the first step toward feeling like yourself again.
References
- Travison TG, Araujo AB, O’Donnell AB, Kupelian V., & McKinlay JB. (2007). A Population-Level Decline in Serum Testosterone Levels in American Men. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 92(1): 196-202.
- Marriott RJ, Murray K, Hankey GJ, Manning L, Dwivedi G, Wu FCW, & Yeap BB. (2021). Longitudinal changes in serum testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin in men aged 40-69 years from the UK Biobank.
- Shigehara K, Izumi K, Kadono Y, & Mizokami A. (2021). Testosterone and bone health in men: A narrative review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 10(3): 530.
- Stanworth RD, & Jones TH. (2008). Testosterone for the ageing male: Current evidence and recommended practice. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 3(1): 25-44.